The Importance of Outdoor Learning Spaces for Students
Topics

We’ve all had the experience of truly purposeful, authentic learning and know how valuable it is. Educators are taking the best of what we know about learning, student support, effective instruction, and interpersonal skill-building to completely reimagine schools so that students experience that kind of purposeful learning all day, every day.
Outdoor learning fosters a deeper connection to the world around students, promotes their physical activity, and provides a unique and enriching way to engage with the curriculum.
Innovations in teaching and learning have had little impact on modern space planning and school architecture. We know that students and teachers do better when they have variety, flexibility, and comfort in their environment. This series examines how next generation learning spaces impact the learning experience for students and their teachers. If you have the opportunity to design a new school building or renovate an existing building, or if you are interested in using space better in your school, this series can help ensure that the physical spaces in your building promote the skills students need to thrive and contribute to an ever-changing global society.
Outdoor learning is an educational approach that takes place outside the traditional classroom setting, where students engage with nature and the environment to enhance their learning experiences. It can involve a wide variety of activities, from field trips and nature walks to hands-on projects and outdoor classrooms. By immersing students in nature, outdoor learning fosters a deeper connection to the world around them, promotes physical activity, and provides a unique and enriching way to engage with the curriculum.
Outdoor learning offers a valuable opportunity for students to connect with the natural world, foster physical and mental well-being, and engage in hands-on, experiential learning. It encourages creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking while promoting environmental awareness and healthy lifestyles. By integrating outdoor learning into the educational experience, schools can provide a well-rounded, dynamic, and exciting approach to learning that prepares students for both academic success and responsible citizenship.
Learning happens everywhere. Outdoor learning increases student activity levels and awareness, authentic problem-solving opportunities, and team collaboration projects and group activities. The outdoors can provide a full range of learning activities. Outdoor learning spaces may include gardens and horticulture, natural environmental studies, weather, solar exploration, and many more learning opportunities.
Flexible indoor/outdoor spaces can open up with glass garage doors, folding glass walls, or stages that face a gym inside and an amphitheater outside. Also hang canvas sail cloths for shade, hang granite slabs as outdoor chalkboards, install adjustable fixed angle photovoltaic panels with individual microinverters for science experiments, water pumps and runnels for water studies, and analemmatic sundials for the students to measure time and sun path.
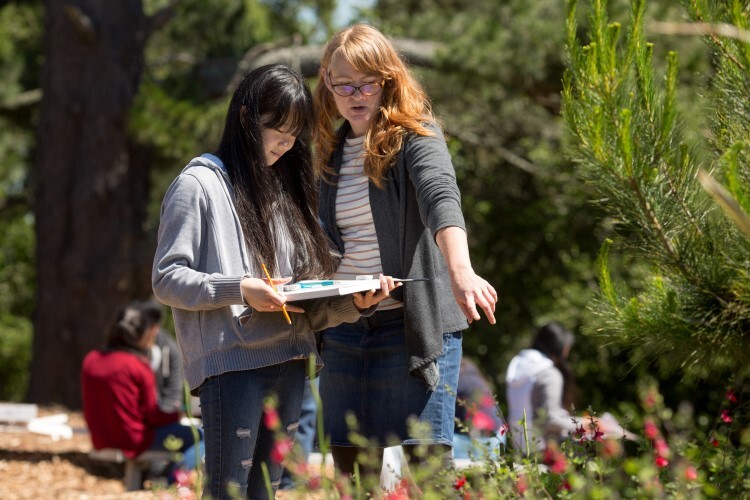

In a lesson outside, a Skyline High School (California) teacher provides feedback on a student's work. Credit: Allison Shelley/The Verbatim Agency for EDUimages, CC BY-NC 4.0.
Key Elements of Outdoor Learning
Experiential Learning: Outdoor learning is based on the concept of experiential learning, where students actively participate in their learning process. Through real-life experiences, they engage with the material in ways that go beyond textbook knowledge. This could include conducting science experiments in the field, studying wildlife, or analyzing environmental issues through direct observation.
Nature-Based Activities: Outdoor learning often involves activities like hiking, gardening, exploring local ecosystems, or outdoor games. These activities allow students to experience the world outside of the classroom, gaining hands-on knowledge and skills.
Environmental Education: A significant aspect of outdoor learning is educating students about the environment, sustainability, and conservation. Learning about ecosystems, weather patterns, natural resources, and climate change in an outdoor setting allows students to better understand the importance of environmental stewardship.
Physical Movement: Outdoor learning encourages physical activity, whether through nature walks, group games, or physical tasks like building shelters or planting gardens. This helps students develop motor skills, coordination, and fitness while learning.
Creativity and Problem-Solving: Many outdoor learning activities encourage creativity and critical thinking. Whether designing a project, problem-solving in teams, or engaging in hands-on tasks, students are prompted to think outside the box, adapt to their surroundings, and work collaboratively to find solutions.
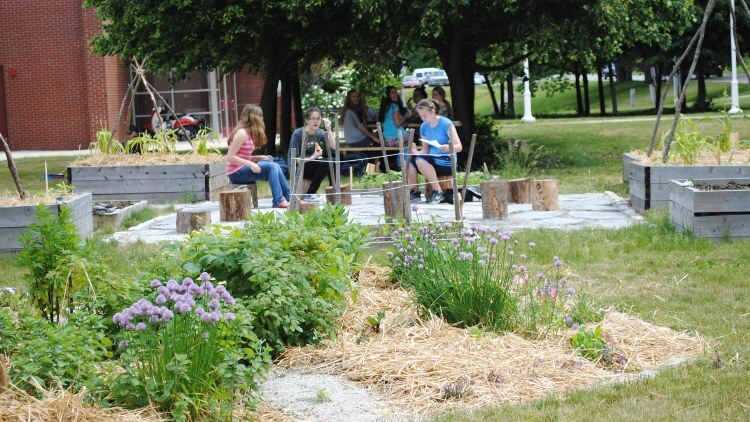

Students collaborate in their South Portland High School vegetable garden and outdoor classroom, South Portland, Maine. Credit: Tania Ferrente on flickr, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Benefits of Outdoor Learning
Improved Engagement and Motivation: Outdoor learning breaks the monotony of the traditional classroom environment, making education more exciting and engaging. Being outside sparks curiosity and encourages students to actively participate in the learning process.
Better Retention of Knowledge: The American Institutes for Research has shown that students who engage in outdoor learning tend to retain information better. This is because the hands-on, real-world experiences provide deeper and more meaningful connections to the material being taught.
Physical and Mental Health Benefits: Spending time outdoors has been linked to numerous physical and mental health benefits, such as reduced stress, improved mood, increased concentration, and better physical fitness. Outdoor learning promotes a healthy lifestyle and encourages students to spend more time being active.
Social and Emotional Development: Outdoor activities often require students to work in groups, which fosters teamwork, communication, and conflict resolution skills. Students also develop a sense of responsibility for their environment and peers, as outdoor learning encourages collaboration and mutual respect.
Increased Creativity and Critical Thinking: The outdoor environment presents endless opportunities for creative thinking. Whether it’s figuring out how to navigate a natural obstacle, brainstorming solutions to environmental challenges, or designing a nature-inspired project, outdoor learning nurtures creativity and problem-solving.
Enhanced Connection with Nature: Outdoor learning fosters an appreciation for the environment. By directly engaging with nature, students develop an understanding of the importance of protecting the planet and the role they can play in sustainability efforts.

Experiential learning goes outside with Quests at Casco Bay High School in Portland, Maine. Credit: Casco Bay High School
Considerations When Planning Outdoor Learning
Weather and Environmental Conditions: Outdoor learning is subject to weather conditions, which can sometimes be unpredictable. Schools need to plan for various weather scenarios and ensure students’ safety during outdoor activities.
Resource and Space Limitations: Not all schools have easy access to natural spaces or outdoor classrooms. For urban schools, finding nearby parks or nature reserves may require extra planning and logistics.
Safety Concerns: Outdoor activities sometimes involve risks, such as navigating uneven terrain or interacting with wildlife. It’s important for educators to have proper safety measures and first aid training in place, as well as clear guidelines for students during outdoor activities.
Curriculum Integration: Outdoor learning must be integrated thoughtfully into the curriculum to ensure that it aligns with educational goals. Teachers may need additional training to design and implement outdoor learning experiences that complement classroom learning.
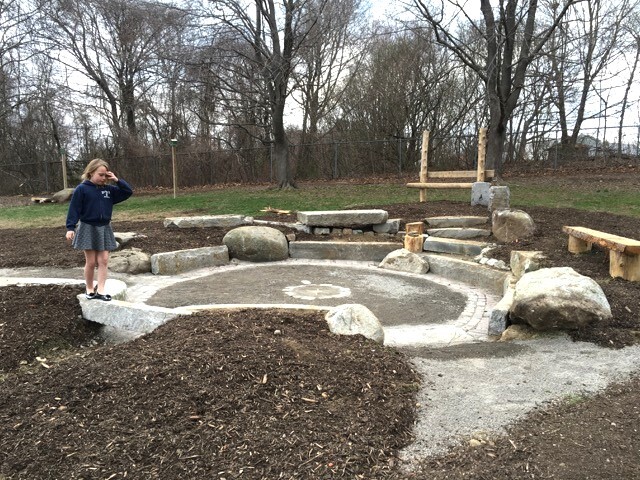

This outdoor classroom area is under construction at Dyer Elementary School in South Portland, Maine. Credit: Laura Newman on flickr, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
How to Implement Outdoor Learning in Schools
Field Trips and Nature Walks: Organizing field trips to local parks, nature reserves, museums, or farms gives students the opportunity to explore the natural world while learning about science, history, or geography.
Outdoor Classrooms: If possible, schools can set up outdoor classrooms or designated spaces on the school grounds. These areas can be used for lessons, discussions, and collaborative activities, providing a natural environment for learning.
Gardening and Environmental Projects: Schools can create gardens or green spaces where students plant and care for vegetables, flowers, or trees. These projects teach responsibility, sustainability, and the science of plants and ecosystems.
STEM Activities in Nature: Teachers can incorporate outdoor learning into STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) lessons by conducting experiments or investigations in nature. For example, students might study the properties of soil, measure plant growth, or explore local weather patterns.
Outdoor Games and Challenges: Physical activities like scavenger hunts, obstacle courses, or team-building exercises can encourage students to work together, solve problems, and improve their physical fitness.
Community Involvement: Schools can collaborate with local organizations, environmental groups, or community members to organize outdoor learning events, nature cleanup projects, or sustainability initiatives.
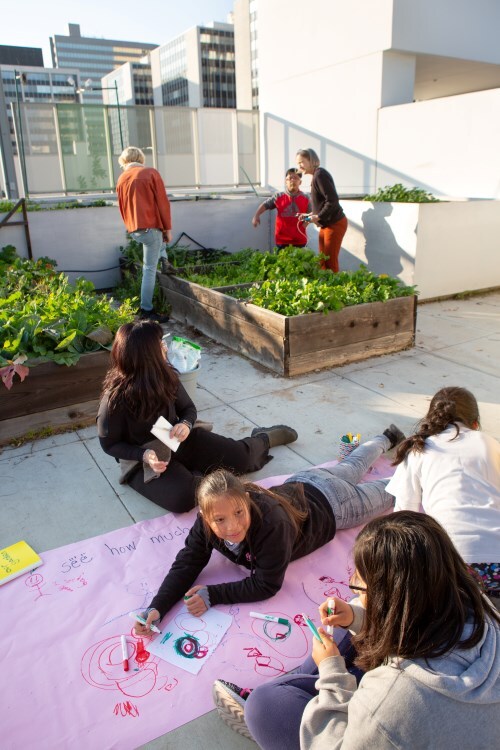

Elementary students at UCLA Community School in California draw pictures inspired by their school’s garden. Credit: Allison Shelley for EDUimages, CC BY-NC 4.0
Learn More
See the whole series about next gen learning spaces.
Photo at top of preschool students studying plants in a school garden by Allison Shelley/The Verbatim Agency for EDUimages, CC BY-NC 4.0.