How Communal Learning Spaces Strengthen Student Collaboration & Community
Topics

We’ve all had the experience of truly purposeful, authentic learning and know how valuable it is. Educators are taking the best of what we know about learning, student support, effective instruction, and interpersonal skill-building to completely reimagine schools so that students experience that kind of purposeful learning all day, every day.
Communal spaces offer schools an interconnected array of options with flexible furniture and technology to support a diversity of learning approaches and help create a collaborative learning community.
Innovations in teaching and learning have had little impact on modern space planning and school architecture. We know that students and teachers do better when they have variety, flexibility, and comfort in their environment. This series examines how next generation learning spaces impact the learning experience for students and their teachers. If you have the opportunity to design a new school building or renovate an existing building, or if you are interested in using space better in your school, this series can help ensure that the physical spaces in your building promote the skills students need to thrive and contribute to an ever-changing global society.
Communal learning in schools offers a dynamic approach that fosters collaboration, social interaction, and a sense of shared responsibility among students. By emphasizing teamwork, inclusivity, and mutual support, communal learning creates a positive and engaging learning environment that benefits both academic achievement and personal growth. Students not only learn from their teachers but also from each other, which builds a strong sense of community within the school. As the world becomes more interconnected, communal learning helps prepare students for the collaborative nature of the modern workforce and society, equipping them with the skills necessary for success in an increasingly globalized world.
A collaborative learning community that is warm and welcoming with transparency into and between learning spaces helps each student find their place. A learning community is a unique collection of places and spaces, both within and beyond the school campus, that help each student thrive, celebrate the collective, and acknowledge that all individuals are part of a greater whole. Communal spaces offer an interconnected array of spatial types with flexible furniture and technology to support a diversity of learning modalities. These flexible spaces create diverse environments from inside to outside that allow students to become ambassadors of their school. They reflect the fact that students DO MATTER.
Learning communities help pave the way for flexible academic groupings, increased independence, self-regulation, and collaboration through student-centered learning. According to the “Learning Pyramid” concept, which outlines different learning styles and their retention rates, students often learn best by doing. In a curriculum aimed at leveraging the power of collaboration, spaces that are adaptable and multifunctional promote highly flexible learning environments. Think about a small group of individuals using their minds, books, technology, and other “quiet” manipulatives to create new knowledge together. Envision a large group with access to a wide variety of manipulatives collaborating to deliver performances or build tangible objects. The facility becomes a valuable resource, with copious gathering, collaborative, and community spaces.
With communal spaces, a school demonstrates an unwavering commitment to the evolving needs of today’s next generation learner. Communal spaces also provide a meaningful civic presence in the community. Recognizing the essential ties between the school and the community, the school can earnestly reflect and celebrate the community it serves with inspirational murals, local heroes, and prominent references to local history and industry adorning the walls. The building can be site-specific and leverage indigenous materials. Every space can be designed to demonstrate optimism, inspire greatness, and encourage lifelong learners. Here students can thrive and aspire to a greater future than they otherwise might have had.
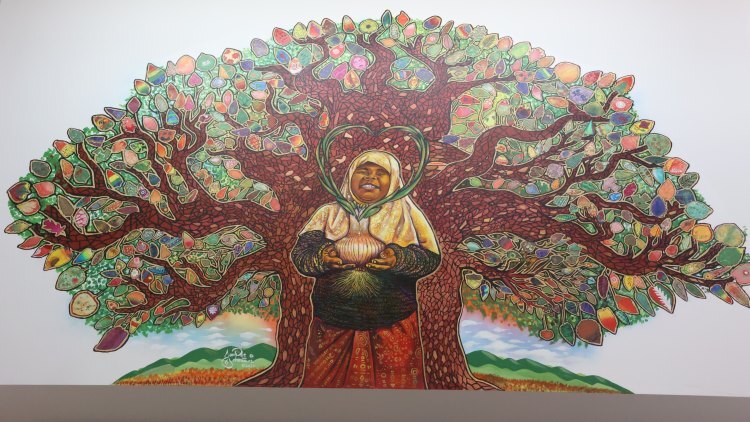

This mural on display in the open communal space upon entry at Winooski Middle High School is one of several ways to welcome the community the school district serves. Credit: Brian Ambrose for NGLC
Communal learning is an educational approach that emphasizes collaboration, shared responsibility, and mutual support among students, teachers, and the school community. It focuses on creating a learning environment where individuals work together toward common goals, drawing on the collective knowledge, experiences, and skills of the group. In communal learning, the learning process becomes a shared journey, where students are not only focused on their own academic achievements but also on supporting and learning from one another.

Credit: westock on Freepik
Key Elements of Communal Learning
Collaboration and Teamwork: Central to communal learning is the idea that students work together as a team. Rather than being isolated learners, students collaborate with their peers to solve problems, complete projects, and share knowledge. This process builds a sense of community and interdependence.
Shared Learning Goals: In a communal learning environment, the entire class or group shares common learning objectives. These goals might be academic, social, or emotional, and students work together to achieve them, fostering a sense of collective responsibility.
Inclusive Environment: Communal learning aims to create an inclusive environment where all students feel valued and are encouraged to participate. Diversity is celebrated, and students learn from the different perspectives and experiences of their peers.
Peer Learning and Mentorship: Peer-to-peer learning is a core aspect of communal learning. Students support each other by explaining concepts, offering feedback, and helping one another. Older or more advanced students may also serve as mentors to younger peers, helping them build confidence and understanding.
Teacher as Facilitator: In a communal learning setting, the teacher’s role is less about traditional lecturing and more about guiding and facilitating the group. Teachers help create opportunities for collaboration, provide support when needed, and encourage students to take ownership of their learning.
Active Participation: Every member of the community is actively involved in the learning process. This means that students are not passive recipients of knowledge, but are engaged in discussions, decision-making, and reflection throughout their learning journey.
Shared Responsibility: In communal learning, students take responsibility for their own learning while also contributing to the learning of others. This sense of shared responsibility helps build a strong learning community where each individual feels accountable to the group.

Credit: Brian Ambrose for NGLC.
Benefits of Communal Learning
Enhanced Social Skills: Collaborative learning helps students develop essential social skills such as communication, teamwork, empathy, and conflict resolution. These skills are crucial both in school and in the workplace, where teamwork and effective interpersonal interactions are often necessary for success.
Improved Academic Outcomes: Research has shown that communal learning can lead to improved academic performance. Students learn more deeply when they explain concepts to peers, discuss ideas, and work together to solve problems. This collaborative approach encourages active engagement, which enhances retention and understanding.
Increased Motivation: When students work together toward common goals, they are more motivated to participate and contribute. The sense of belonging and shared purpose fosters a positive learning environment that encourages students to put in their best effort.
Development of Critical Thinking: Communal learning encourages students to think critically and engage in discussions where they are exposed to different viewpoints. This process challenges their assumptions, promotes problem-solving, and helps them develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Sense of Belonging and Community: A communal learning environment creates a supportive and inclusive atmosphere where students feel like they are part of something larger than themselves. This sense of belonging boosts self-esteem, reduces feelings of isolation, and creates a positive school culture.
Preparation for Real-World Collaboration: In today’s interconnected world, collaboration is a key skill in the workplace and in society. By practicing communal learning, students develop the skills necessary to work in teams, share ideas, and tackle challenges together, which prepares them for future roles in diverse settings.

Credit: seventyfour on freepik
Considerations when Using Communal Spaces for Group Work
Uneven Participation: In communal learning, not all students may participate equally. Some may dominate discussions, while others may withdraw. Teachers need to actively monitor group dynamics and ensure that everyone has an opportunity to contribute.
Group Work Challenges: Collaborative projects can sometimes result in unequal contributions, with some students doing more of the work than others. Teachers can address this by assigning clear roles, setting expectations, and holding students accountable for their individual contributions.
Time Constraints: Communal learning activities, such as group projects and discussions, can take more time than traditional individual tasks. Schools with tight schedules may find it challenging to allocate sufficient time for these activities.
Diverse Learning Styles: Students have different learning preferences, and communal learning may not always accommodate these differences. Some students may prefer independent work, while others may excel in group settings. It’s important to balance group-based activities with opportunities for individual reflection and learning.
Classroom Management: Managing group dynamics and ensuring productive collaboration can be challenging. Teachers need to be skilled in guiding group interactions, resolving conflicts, and ensuring that all students are on task.

Credit: standret on freepik
How to Implement Communal Learning in Schools
Group Projects and Collaborative Assignments: Assign projects that require students to work together to research, create, or solve a problem. These projects can be cross-curricular, integrating subjects such as science, math, history, and language arts. Group work encourages students to share their knowledge and collaborate toward a common goal.
Cooperative Learning Strategies: Use cooperative learning methods such as “Think-Pair-Share,” “Jigsaw,” or “Peer Teaching,” where students work together in pairs or small groups to explore concepts and then share their findings with the class. These strategies encourage active participation and foster collaboration.
Discussion Circles and Group Debates: Encourage students to engage in structured discussions or debates around a central theme or issue. This allows students to hear different perspectives, refine their arguments, and learn from their peers. It also fosters critical thinking and communication skills.
Collaborative Problem-Solving: Present students with real-world problems that require collective problem-solving. These could involve social, environmental, or technological challenges. Working together to find solutions encourages creativity, teamwork, and the application of knowledge across subjects.
Peer Mentoring and Tutoring: Establish peer mentoring or tutoring programs where older students help younger ones. This promotes knowledge sharing, builds leadership skills, and strengthens the sense of community within the school.
Fostering Inclusivity: Ensure that communal learning activities are inclusive and welcoming to all students, regardless of their background, abilities, or learning styles. Create a classroom culture where diversity is celebrated and all voices are heard.
Reflection and Feedback: After communal learning activities, provide opportunities for students to reflect on their experiences. Ask them to consider how the group worked together, what they learned from one another, and how they can improve in future collaborative efforts. Feedback is crucial for helping students grow in their ability to work with others.
Learn More
See the whole series about next gen learning spaces.
Photo at top: The EdHub is a communal space at the entry to this Kentucky K-12 school includes transparent views to the exterior, fixed and movable flat-panel technology, comfortable variety seating with options to sit or stand, and worktables for project-based learning. Courtesy of Eminence K-12.